Specifying Target Container¶
Running a specific action requires to specify a target container, in confines of which this action is executed. Thus, it is possible to specify a particular container, all containers within a layer by the nodeGroup value, or all containers of the same type by the nodeType value.
Particular Container¶
The nodeId parameter is used to specify a particular container for the action execution. If you know the Node ID of your container (displayed at the Virtuozzo Application Platform dashboard next to the required node), you can set it statically as follows.
writeFile:
- nodeId: 123
path: /var/www/webroot/hw.txt
body: Hello World!
{
"writeFile": [
{
"nodeId": "123",
"path": "/var/www/webroot/hw.txt",
"body": "Hello World!"
}
]
}
writeFile:
- nodeId: ${nodes.apache2[0].id}
path: /var/www/webroot/hw.txt
body: Hello World!
{
"writeFile": [
{
"nodeId": "${nodes.apache2[0].id}",
"path": "/var/www/webroot/hw.txt",
"body": "Hello World!"
}
]
}
All Containers By Group¶
The nodeGroup parameter is used to specify all containers within a specific layer.
The Virtuozzo Application Platform supports the following predefined nodeGroup values:
-
bl
-
cp
-
cache
-
sqldb
-
nosqldb
-
storage
-
vds (for VPS)
-
build
Actions for the specified nodeGroup are executed successively one by one. For Docker containers the nodeGroup value is not predefined, therefore, you can state it to any value above or your custom one.
Note
If you state a custom nodeGroup value for Docker containers, the corresponding container is placed to the Extra layer. Subsequently, this nodeGroup value can be used within the same-named actions field to point to the particular Extra layer.
All Containers By Type¶
The nodeType parameter is used to specify all containers that are built upon the same software stacks.
Examples
Using the nodeType parameter while performing the writeFile action.
writeFile:
nodeType: apache2
path: /tmp/example.txt
body: Hello World
{
"writeFile": {
"nodeType": "apache2",
"path": "/tmp/example.txt",
"body": "Hello World"
}
}
writeFile- action to write data to the filenodeType- parameter that specifies the node typepath- parameter that specifies the path to the filebody- data that is written to the file
Using the engine and nodeType parameters while creating a new environment.
type: install
name: install Tomcat7 node
engine: java7
nodes:
nodeType: tomcat7
{
"type": "install",
"name": "install Tomcat7 node",
"engine": "java7",
"nodes": {
"nodeType": "tomcat7"
}
}
engine- parameter that specifies the engine versionnodeType- parameter that specifies the node type
Selector Types¶
There are three alternative approaches, provided to specify a target container in a manifest:
- specifying a target container within a name of an action (node selectors)
Through the following example, a new file is created in the compute layer ([cp]) and a new directory is created in the compute ([cp]) and balancer ([bl]) layers, and container with the Node ID 123. Actions for the specified containers are executed in the declared order.
- createfile [cp]:
path: /tmp/test.txt
- createDirectory [cp,bl,123]:
path: /tmp/test
[
{
"createFile [cp]": {
"path": "/tmp/test.txt"
}
},
{
"createDirectory [cp,bl,123]": {
"path": "/tmp/test"
}
}
]
A defined action in manifest could be executed in all nodes of all layers within an environment where JPS is executed. For example:
type: update
name: cmd in all nodes
onInstall:
cmd [*]: echo hello world!
{
"type": "update",
"name": "cmd in all nodes",
"onInstall": {
"cmd [*]": "echo hello world!"
}
}
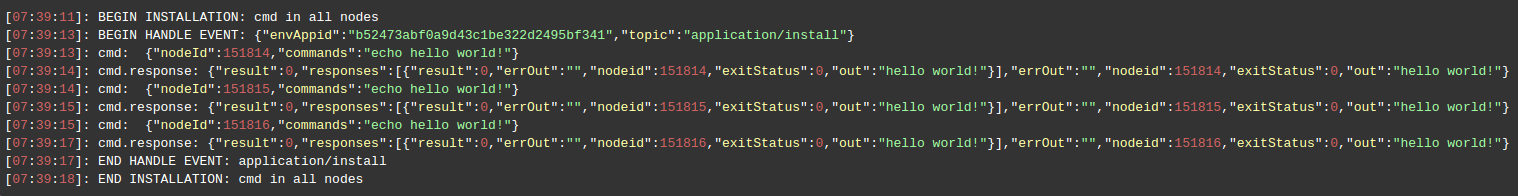
There is a console log screen which displays that cmd action has been executed in all nodes by unique identifier one by one:
- specifying a target container next to the performed action
Through the following example, the createFile and createDirectory actions are applied to the specified nodeGroup, namely the compute layer ([cp]).
- createFile:
path: /tmp/test.txt
createDirectory:
path: /tmp/test
nodeGroup: cp
[
{
"createFile": {
"path": "/tmp/test.txt"
},
"createDirectory": {
"path": "/tmp/test"
},
"nodeGroup": "cp"
}
]
- specifying a target container as a parameter in the actions object
Learn more on this parameter within the Custom Actions documentation page.
Note
Node selectors have higher priority than containers specified next to the action, but lower than parameters set in the actions object.
If you specify all three parameters (nodeId, nodeGroup, and nodeType), actions for indicated containers are executed in the following order: nodeId -> nodeGroup -> nodeType.
NodeGroup Aliases¶
An existed nodes in environments can be targeted not only by their defined *nodeGroup*s and by aliases. That aliases could be defined in manifests like in example:
type: update
name: Alias for nodeGroup
nodeGroupAlias:
cp: sqldb2
onInstall:
log: ${nodes.sqldb2.id}
{
"type": "update",
"name": "Alias for nodeGroup",
"nodeGroupAlias": {
"cp": "sqldb2"
},
"onInstall": {
"log": "${nodes.sqldb2.id}"
}
}
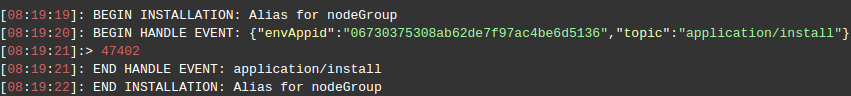
In the example above JPS add-on with type update could be applied on any existing environment. In this case all compute nodes with nodeGroup cp can be called by aliases (Nodes with nodeGroup sqldb2 are absent in environment). So the example result is displayed in the screen:
Note
nodeGroupAlias option works only within current JPS manifest.
Supported Stacks¶
The supported software stacks are categorized in the table below with specified names and aliases that can be used within Cloud Scripting, as well as the links to the available tags.
| nodeGroup | Supported nodeType Values (Aliases) | Supported Tags Link |
|---|---|---|
| bl | nginx-dockerized (nginx), varnish-dockerized (varnish), haproxy(haproxy2), apache-lb (apache-balancer), litespeedadc (litespeedadc2, litespeedadc3) | Load-Balancers |
| cp | dotnet (dotnet5, dotnet3, dotnet7, dotnet6), apache (apache2), apache-python (apache2-python), apache-ruby (apache2-ruby), glassfish (glassfish5, glassfish6, glassfish3), golang, javaengine, jenkins (jenkins2), jetty (jetty10, jetty9, jetty11), lemp, litespeedphp (litespeedphp5, litespeedphp6), llsmp (llsmp6, llsmp5), nginxphp-dockerized (nginxphp), nginxruby (nginx-ruby), nodejs (nodejs14-supervisor, nodejs14-npm, nodejs16-forever, nodejs14-pm2, nodejs16-supervisor, nodejs16-pm2, nodejs14-forever, nodejs16-npm), payara (payara5, payara3), springboot, tomcat (tomcat85, tomcat9, tomcat10, tomcat8, tomcat11, tomcat6, tomcat7), tomee-dockerized (tomee), wildfly (wildfly26-preview, wildfly24, wildfly26, wildfly25, wildfly25-preview, wildfly27, wildfly24-preview, wildfly27-preview) | Application Servers |
| sqldb, nosqldb | couchbase, mariadb-dockerized (mariadb10, mariadb1010, mariadb106, mariadb107, mariadb104, mariadb109, mariadb108, mariadb103, mariadb105), mongodb-dockerized (mongodb), mysql (mysql5, mysql8), opensearch (opensearch2, opensearch1), perconadb (percona5.7, percona8, percona5, percona8.0), postgresql (postgres14, postgres11, postgres12, postgres13), redis (redis7, redis6) | Databases |
| vps, cache, build, storage, extra | centos-vps (centos7), debian-vps (debian10, debian9, debian11), dockerengine, kubernetes, logstash (logstash8, logstash7), maven (maven3), memcached-dockerized (memcached), opensearchdashboards (opensearchdashboards1, opensearchdashboards2), pgpool2 (pgpool2-4), proxysql, storage, ubuntu-vps (ubuntu22, ubuntu16, ubuntu20, ubuntu18), windows2019 | Additional Stacks |
Note
In case the root privileges are required within the certified template, it should be created as custom docker via image parameter. If so, take into account that some functionality/automation won’t be available such as Custom SSL, Managed Firewall, etc. To create custom docker follow the Supported Tags Link column to get the proper name of certified Virtuozzo docker images.
| Stacks | Java | PHP | Ruby | Python | Nodejs | .NET | Go |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| engine | adoptopenjdk-8 adoptopenjdk-11 adoptopenjdk-13 adoptopenjdk-14 adoptopenjdk-15 adoptopenjdk-16 correttojdk-8 correttojdk-11 correttojdk-15 correttojdk-16 correttojdk-17 correttojdk-18 correttojdk-19 dragonwell-8 graalvm-19 graalvm-21 graalvm-22 jdk-8 jdk-11 openj9-8 openj9-11 openj9-14 openj9-15 openj9-16 openjdk-8 openjdk-11 openjdk-13 openjdk-14 openjdk-15 openjdk-16 openjdk-17 openjdk-18 openjdk-19 openjdk-20 openjdk-21 temurinjdk-8 temurinjdk-11 temurinjdk-17 temurinjdk-18 temurinjdk-19 zulujdk-8 zulujdk-11 zulujdk-13 zulujdk-14 zulujdk-15 zulujdk-16 zulujdk-17 zulujdk-18 zulujdk-19 |
php7.4 php8.0 php8.1 |
ruby2.7 ruby3.0 ruby3.1 |
python3.6 python3.7 python3.8 python3.9 python3.10 python3.11 |
nodejs14-npm nodejs14-forever nodejs14-pm2 nodejs14-supervisor nodejs16-npm nodejs16-forever nodejs16-pm2 nodejs16-supervisor |
dotnet3 dotnet5 dotnet6 dotnet7 |
go14 go15 go16 go17 go18 go19 |
Note
The list of supported software stacks can vary depending on your Virtuozzo Application Platform version - it can be checked at your dashboard.
Selecting Hardware Hosts¶
There is an ability in Virtuozzo Application Platform to select the hardware for the user's application with the help of the multi zones approach. If a user is aware all of the labels assigned for the hardware hosts within the platform he can decide which hosts across all of the available regions can be used to install the user's environment.
Hardware host selection is performed by distribution parameter which defines the logic in the layer specifics, which consist of the following two options:
-
zones- sets a filter for allowed zones (groups of hosts custom-defined by labels) in the “{name}: {value}” format, e.g. zones: [{provider: azure}, {provider: amazon}] -
mode- defines the behavior in case of the target zone unavailability-
SOFT - the operation should proceed on the next zone/host defined by the multi zones algorithm (this option is used by default)
-
STRICT - the operation should be terminated with an error
-
Note
- the distribution is performed in the within of a single host group (i.e. user environment region)
- the default zone {name} can be skipped when providing zones parameter, i.e. the zones: [“a”, “b”] and zones: [{zone: a}, {zone: b}] expressions are equal
- if zones with two or more {value} are specified for a single {name}, hosts with either of these values will be allowed for distribution
- if zones with two or more {name} are specified, only hosts with all these labels will be allowed for distribution
- if zones are not specified, distribution is performed across all hosts
- the maximum number of elements in zones is 10
- the maximum number of unique {value} per each {name} is 20
For example, the distribution configured in the following package ensures nodes are created only on the hosts with the disk: ssd label.
name: "multi-zone"
type: install
nodes:
nodeType: docker
fixedCloudlets: 1
flexibleCloudlets: 8
image: jelastic/tomcat:latest
count: 2
distribution:
mode: SOFT
zones:
- disk: ssd
{
"name": "multi-zone",
"type": "install",
"nodes": {
"nodeType": "docker",
"fixedCloudlets": 1,
"flexibleCloudlets": 8,
"image": "jelastic/tomcat:latest",
"count": 2,
"distribution": {
"mode": "SOFT",
"zones": [
{
"disk": "ssd"
}
]
}
}
}
The zones parameter can be provided dynamically defining pair of label name and value via user interface.
For example:
name: "multi-zone"
type: install
settings:
fields:
- hideLabel: false
type: string
caption: Label name
name: labelname
- hideLabel: false
type: string
caption: Label value
name: labelvalue
nodes:
- nodeType: tomcat
cloudlets: 6
distribution:
mode: SOFT
zones:
- "${settings.labelname}": "${settings.labelvalue}"
{
"name": "multi-zone",
"type": "install",
"settings": {
"fields": [
{
"hideLabel": false,
"type": "string",
"caption": "Label name",
"name": "labelname"
},
{
"hideLabel": false,
"type": "string",
"caption": "Label value",
"name": "labelvalue"
}
]
},
"nodes": [
{
"nodeType": "tomcat",
"cloudlets": 6,
"distribution": {
"mode": "SOFT",
"zones": [
{
"${settings.labelname}": "${settings.labelvalue}"
}
]
}
}
]
}
What’s next?
-
Explore the list of available Actions
-
See the Events list the actions can be bound to
-
Find out the list of Placeholders for automatic parameters fetching
-
Read how to integrate your Custom Scripts
-
Learn how to customize Visual Settings