Control Flows: Conditions and Iterations¶
Comparison and Logical operators are used in conditional statements and serve to test for ture or false.
Comparison Operators¶
The Comparison operators are used in logical statements to determine equality or difference between variables or values.
Let's assume that x = 5. The table below explains the comparison operators:
| Operator | Description | Comparing | Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | equal to | x == 8 | false |
| == | equal to | x == 5 | true |
| == | equal to | x == "5" | true |
| === | equal value and equal type | x === 5 | true |
| === | equal value and equal type | x === "5" | false |
| != | not equal | x != 8 | true |
| !== | not equal value or not equal type | x !== 5 | false |
| !== | not equal value or not equal type | x !== "5" | true |
| !== | not equal value or not equal type | x !== 8 | true |
| > | grater than | x > 8 | false |
| < | less than | x < 8 | true |
| >= | grater than or equal to | x >= 8 | false |
| <= | less than or equal to | x <= 8 | true |
Logical Operators¶
The logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values. Let's take that x = 6 and y = 3. The table below explains the logical operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| && | and | (x < 10 && y > 1) is true |
| == | or | (x == 5 |
| == | not | !(x == y) is true |
Conditions¶
The main conditional statement is if. Within this parameter, all the available placeholders and their objective JavaScript mappings can be used.
For example
if ('${env.protocol}' == 'http')
or
if (env.protocol == 'http')
The main iterable object is ForEach. Both if and ForEach can be of any nesting level.
-
If condition is specified incorrectly, the actions inside if statement are not executed. Herewith, the Cloud Scripting Console returns the ‘invalid condition’ message with the root cause explanation. The application installer proceeds to the next action.
-
If condition is valid, but is not executed, the 'condition is not met' message is logged.
Examples
-
Comparing global variables
type: update name: Comparing global variables globals: p1: 1 p2: 2 onInstall: - if (globals.p1 < globals.p2): if (user.uid > 1): log: "## p1 < p2 and ${user.email} is not a platform owner"{ "type": "update", "name": "Comparing global variables", "globals": { "p1": 1, "p2": 2 }, "onInstall": [ { "if (globals.p1 < globals.p2)": { "if (user.uid > 1)": { "log": "## p1 < p2 and ${user.email} is not a platform owner" } } } ] }
Checking environment status
onInstall:
if (env.status == 1):
log: "## Environment is running"
{
"onInstall": {
"if (env.status == 1)": {
"log": "## Environment is running"
}
}
}
Checking Jelastic SSL status
onInstall:
if(!${env.ssl}):
log: "## SSL Disabled"
{
"onInstall": {
"if(!${env.ssl})": {
"log": "## SSL Disabled"
}
}
}
Validating environment domain
onInstall:
if (/^env-/.test(env.domain)):
log: "## Env domain begins with env-: ${env.domain}"
{
"onInstall": {
"if (/^env-/.test(env.domain))": {
"log": "## Env domain begins with env-: ${env.domain}"
}
}
}
Checking compute node OS type and balancer presence
onInstall:
if (nodes.cp && nodes.cp[0].osType == 'LINUX'):
log: "## Environment has compute node based on Linux"
if (nodes.bl && nodes.bl[0].nodeType == 'nginx' && nodes.cp.length > 1):
log: "## Environment has Nginx balancer and more than one compute node"
{
"onInstall": {
"if (nodes.cp && nodes.cp[0].osType == 'LINUX')": [
{
"log": "## Environment has compute node based on Linux"
},
{
"if (nodes.bl && nodes.bl[0].nodeType == 'nginx' && nodes.cp.length > 1)": {
"log": "## Environment has Nginx balancer and more than one compute node"
}
}
]
}
}
Nested Conditions¶
Nesting of two if conditional statements - the first one is checking an environment for two compute nodes presence. If the nodes are available, the second one is checking the presence of the external IP address on the first balancer node and is logging the correspondent messages.
type: update
name: Nesting example
onInstall:
if (${nodes.cp[1].id}):
- cmd [${nodes.cp[1].id}]: echo "Environment consists of two compute nodes" >> /tmp/result.txt
- if (/^[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}/.test("${nodes.bl[0].extips}")):
cmd [${nodes.cp[0].id}]: echo "Balancer node with external IP address!" >> /tmp/result.txt
{
"type": "update",
"name": "Nesting example",
"onInstall": {
"if (${nodes.cp[1].id})": [
{
"cmd [${nodes.cp[1].id}]": "echo \"Environment consists of two compute nodes\" >> /tmp/result.txt"
},
{
"if (/^[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}.[0-9]{2,3}/.test(\"${nodes.bl[0].extips}\"))": {
"cmd [${nodes.cp[0].id}]": "echo \"Balancer node with external IP address!\" >> /tmp/result.txt"
}
}
]
}
}
The operation result can be located within a result.txt file that is automatically created in the master node (i.e. the first cp node) tmp directory.
Environment consists of two compute nodes
Balancer node with external IP address!
- Checking balancer stack type
type: update name: Nginx stack onInstall: if (nodes.bl[0].nodeType == 'nginx'): - script: | return { result: 0, error: "Environment balancer node is NGINX stack"};{ "type": "update", "name": "Nginx stack", "onInstall": { "if (nodes.bl[0].nodeType == 'nginx')": [ { "script": "return { result: 0, error: \"Environment balancer node is NGINX stack\"};" } ] } }
Else¶
In case the conditional statement should be complemented by the opposite comparison and respective action the else conditional operator can be accommodated.
type: install
name: '[CS:Conditions] - action "else"'
globals:
a: 1
b: 2
onInstall:
- log: "-- else condition test --"
- if (false):
assert: false
- else:
assert: true
- if (globals.a === 1):
assert: true
- else:
assert: false
- log: "-- nested conditions test --"
- if ('${globals.b}' === '2'):
if (false):
assert: false
- else:
assert: false
- log: "-- conditions position test --"
- if (false):
assert: true
- log: test
- else:
assert: false
- log: "-- invalid condition test --"
- if ( ):
assert: false
- else:
assert: false
{
"type": "install",
"name": "[CS:Conditions] - action 'else'",
"globals": {
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
"onInstall": [
{
"log": "-- else condition test --"
},
{
"if (false)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"else": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"if (globals.a === 1)": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"else": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"log": "-- nested conditions test --"
},
{
"if ('${globals.b}' === '2')": {
"if (false)": {
"assert": false
}
}
},
{
"else": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"log": "-- conditions position test --"
},
{
"if (false)": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"log": "test"
},
{
"else": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"log": "-- invalid condition test --"
},
{
"if ( )": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"else": {
"assert": false
}
}
]
}
Elif¶
An elif is a combination of if and else. Similar to else, it extends the if statement to execute a different statement in case the original if expression evaluates to FALSE. However, unlike else, it will execute that alternative expression only if the elif conditional expression evaluates to TRUE. There may be several elif within the same if statement. The first elif expression (if several exist) that evaluates to TRUE would be executed and the others will be skipped.
type: install
name: '[CS:Conditions] - action "elif"'
globals:
a: 1
b: 2
onInstall:
- log: "-- elif positive test --"
- if (globals.a == 2):
assert: false
- elif (globals.a == 3):
assert: false
- elif (globals.a == 1):
assert: true
- elif (globals.a == 1):
assert: false
- elif (globals.b == 2):
assert: false
- else:
assert: false
- log: "-- elif negative test --"
- if (globals.a == 1):
assert: true
- elif (globals.a == 1):
assert: false
- elif (globals.a == 1):
assert: false
{
"type": "install",
"name": "[CS:Conditions] - action 'elif'",
"globals": {
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
"onInstall": [
{
"log": "-- elif positive test --"
},
{
"if (globals.a == 2)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"elif (globals.a == 3)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"elif (globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"elif (globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"elif (globals.b == 2)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"else": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"log": "-- elif negative test --"
},
{
"if (globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"elif (globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": false
}
},
{
"elif (globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": false
}
}
]
}
Single line if statement¶
Another if-else combination can be represented as a single if statement when multiple conditions are required to be checked and the statements nesting is not mandatory. It is applicable if any condition or all of the conditions in the statement may lead to the same outcome. For example:
type: install
name: '[CS:Conditions] - action single line "if"'
globals:
a: 1
b: 2
onInstall:
- log: "-- single line if test --"
- if ((globals.b == 2) && (globals.a == 1) && (globals.a == 1)):
assert: true
- log: "-- another single line if test --"
- if (globals.a == 2 || globals.a == 3 || globals.a == 1):
assert: true
{
"type": "install",
"name": "[CS:Conditions] - action single line \"if\"",
"globals": {
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
"onInstall": [
{
"log": "-- single line if test --"
},
{
"if ((globals.b == 2) && (globals.a == 1) && (globals.a == 1))": {
"assert": true
}
},
{
"log": "-- another single line if test --"
},
{
"if (globals.a == 2 || globals.a == 3 || globals.a == 1)": {
"assert": true
}
}
]
}
Iterations¶
ForEach¶
The main iterable object is ForEach with the following map.
env:
nodes: []
contexts: []
extdomains: []
nodes: {}
settings: {}
license: {}
event:
params: {}
response: {}
this: {}
{
"env": {
"nodes": [],
"contexts": [],
"extdomains": []
},
"nodes": {},
"settings": {},
"license": {},
"event": {
"params": {},
"response": {}
},
"this": {}
}
settings[optional] - values of the fields that are predefined within a user settings formlicense [optional]- link to fetch parameters that are specified within the prepopulate custom script. It enables to customize default field values and can be further initialized through the$(license.{any_name}placeholder within a manifest.event [optional]- object with events that can be of two types, triggering a particular action before or after the event executionthis [optional]- object with parameters that are transmitted within the procedure body. See the full list of available placeholders on this parameter.
Iteration can be executed by env.nodes, nodes, env.contexts, and env.extdomains objects.
Iteration set by env.extdomains.
forEach(env.extdomains):
- writeFile:
nodeGroup: cp
path: /var/lib/jelastic/keys/${@i}.txt
body: hello
{
"forEach(env.extdomains)": [
{
"writeFile": {
"nodeGroup": "cp",
"path": "/var/lib/jelastic/keys/${@i}.txt",
"body": "hello"
}
}
]
}
@i- default iterator nameenv.extdomains- bound external domains
Iteration set by env.contexts.
forEach(env.contexts):
writeFile [cp]:
path: /var/lib/jelastic/keys/${@i.context}.txt
body: 1
{
"forEach(env.contexts)": {
"writeFile [cp]": {
"path": "/var/lib/jelastic/keys/${@i.context}.txt",
"body": "1"
}
}
}
env.contexts- list of contexts (applications) deployed to an environment
The example of scaling nodes.
type: update
name: Scaling Example
onAfterScaleIn [nodeGroup:cp]: ScaleNodes
onAfterScaleOut [nodeGroup:cp]: ScaleNodes
actions:
ScaleNodes:
forEach(nodes.cp):
cmd [bl]:
- {commands to rewrite all Compute nodes internal IP addresses in balancer configs. Here balancer node is NGINX}
- /etc/init.d/nginx reload
{
"type": "update",
"name": "Scaling Example",
"onAfterScaleIn[nodeGroup:cp]": "ScaleNodes",
"onAfterScaleOut[nodeGroup:cp]": "ScaleNodes",
"actions": {
"ScaleNodes": {
"forEach(nodes.cp)": {
"cmd [bl]": [
"{commands to rewrite all Compute nodes internal IP addresses in balancer configs. Here balancer node is NGINX}",
"/etc/init.d/nginx reload"
]
}
}
}
}
By All Nodes¶
Iteration by all nodes in an environment.
Iteration set by env.nodes.
forEach(env.nodes):
cmd [${@i.id}]: echo ${@i.address} > /tmp/example.txt
{
"forEach(env.nodes)": {
"cmd [${@i.id}]": "echo ${@i.address} > /tmp/example.txt"
}
}
By Compute Nodes¶
Iteration by compute nodes with a custom iterator name.
forEach(cp:nodes.cp):
cmd [${@cp.id}]: echo ${@cp.address} > /tmp/example.txt
{
"forEach(cp:nodes.cp)": {
"cmd [${@cp.id}]": "echo ${@cp.address} > /tmp/example.txt"
}
}
-
@cp [optional] - custom iterator name. Also, target nodes can be set by type -{@cp.nodeType}*, or group - *{@cp.nodeGroup}.
Custom iterator name can be used for nesting cycles one into another.
type: update
name: execution actions
onInstall:
forEach(item:env.nodes):
forEach(secondItem:env.nodes):
log: ${@@item} - ${@@secondItem} - ${@}
{
"type": "update",
"name": "execution actions",
"onInstall": {
"forEach(item:env.nodes)": {
"forEach(secondItem:env.nodes)": {
"log": "${@@item} - ${@@secondItem} - ${@}"
}
}
}
}
${@}- iterator number current loop${@@item}- iterator number of the first loop${@@secondItem}- iterator number of the second loop
In this case, every environment node will have only one conjunction by Node ID.
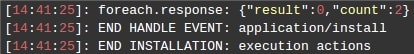
The ForEach execution is recorded in the user console log file for convenient code debugging.
What's next?
-
Read how to integrate your Custom Scripts
-
Learn how to сreate your custom Add-Ons
-
Find out how to handle Custom Responses
-
See how to customize Visual Settings
-
Examine a bunch of Samples with operation and package examples
-
See the Troubleshooting for helpful tips and specific suggestions